AWS:Set up account: Difference between revisions
| (29 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[ | * Tutorial 1 AWS:Set up account THIS TUTORIAL | ||
* Tutorial 2: [[AWS:Upload files for docking]] | |||
* Tutorial 3: [[AWS:Submit docking job]] | |||
* Tutorial 4: [[AWS:Merge and download results]] | |||
* Tutorial 5: [[AWS:Cleanup]] | |||
= Installation = | = Installation = | ||
Docker is required to run the aws-setup scripts. https://www.docker.com/get-started/ | Docker is required to run the aws-setup scripts. https://www.docker.com/get-started/. You can install docker desktop to your personal machine, or log on to a machine where docker is already installed. | ||
An Amazon AWS account is also required, with payment attached. https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/create-and-activate-aws-account/ | An Amazon AWS account is also required, with payment attached. https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/create-and-activate-aws-account/ | ||
| Line 14: | Line 15: | ||
<nowiki> | <nowiki> | ||
docker pull | docker pull dockingorg/aws-setup | ||
docker run -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock --rm -it | docker run -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock --rm -it dockingorg/aws-setup</nowiki> | ||
Explanation of arguments: | Explanation of arguments: | ||
| Line 30: | Line 31: | ||
<nowiki> | <nowiki> | ||
docker run --privileged -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock -it | docker run --privileged --rm -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock -it dockingorg/aws-setup</nowiki> | ||
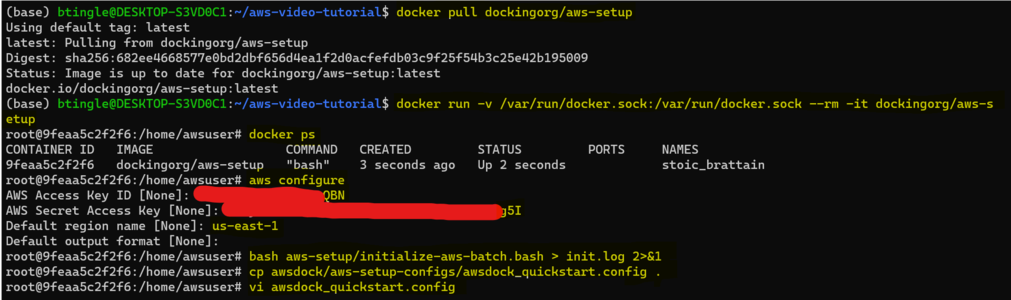
[[File:Step1-docktut-again.png|x300px|Example session depicting pulling the aws-setup image, running it, authenticating with AWS, and initializing the account.]] | |||
= Container Environment = | = Container Environment = | ||
The container | The container uses the ubuntu distribution. Some utilities such as curl and vi are installed so you can download files and edit them. You can also install whatever software you like using "apt install", e.g "apt install git". | ||
If you have files you'd like to access from the container, you can link them in using the docker "-v" option. By default we link the docker socket using this option ("-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock"), but you can link any number of directories or files in this manner. For example, if you would like the contents of the "/tmp" directory on your local machine to be available under "/temp" in the docker image, you would add the following option to your "docker run" command: "-v /tmp:/temp", for a final command of: | If you have files you'd like to access from the container, you can link them in using the docker "-v" option. By default we link the docker socket using this option ("-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock"), but you can link any number of directories or files in this manner. For example, if you would like the contents of the "/tmp" directory on your local machine to be available under "/temp" in the docker image, you would add the following option to your "docker run" command: "-v /tmp:/temp", for a final command of: | ||
<nowiki>docker run -v /tmp:/temp -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock -it | <nowiki>docker run -v /tmp:/temp -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock --rm -it dockingorg/aws-setup:latest</nowiki> | ||
If you're an advanced user and you'd like to create your own version of the aws-setup image with certain software preinstalled, you can request us for access to the aws-setup repository, which contains the scripts and Dockerfile we use to set up the docker image. You can also build your own image using our aws-setup image as a base. | If you're an advanced user and you'd like to create your own version of the aws-setup image with certain software preinstalled, you can request us for access to the aws-setup repository, which contains the scripts and Dockerfile we use to set up the docker image. You can also build your own image using our aws-setup image as a base. | ||
| Line 59: | Line 48: | ||
== Setup == | == Setup == | ||
=== Credentials & Region === | |||
When you enter the docker image, you will be in /home/awsuser. There should be two directories in front of you, aws-setup and awsdock. We start off by going into the aws-setup directory and configuring our AWS credentials. (This needs to be done every time you log in to the container) | When you enter the docker image, you will be in /home/awsuser. There should be two directories in front of you, aws-setup and awsdock. We start off by going into the aws-setup directory and configuring our AWS credentials. (This needs to be done every time you log in to the container) | ||
| Line 69: | Line 60: | ||
Make sure to save your keys somewhere safe that you will remember!! | Make sure to save your keys somewhere safe that you will remember!! | ||
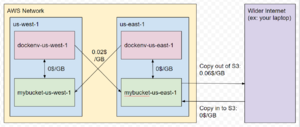
Next, you'll be prompted on which region you would like to use. | Next, you'll be prompted on which AWS region you would like to use. If this is your first environment, set the region to us-east-1. Our lab's molecule data S3 bucket (zinc3d) is also located in this region, so this is the most economical region to run docking jobs in, due to the cost of moving data between AWS regions. (see diagram) | ||
[[File:S3pricing.png|thumb|Diagram showing the cost of transferring S3 data between regions and across to the internet]] | |||
More info on regions & region codes here: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/using-regions-availability-zones.html | |||
The last prompt sets the preferred output format- feel free to leave this blank, or set it to "json". | |||
=== S3 Bucket === | |||
You | An S3 bucket is a virtual hard drive that your AWS resources can access from anywhere. You will need to create one on your account prior to creating your AWS environment. Follow the amazon tutorial on how to do this: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/userguide/create-bucket-overview.html | ||
<b>The quickstart guide will show you how to create an AWS environment in us-east-1, so it is best to create your S3 bucket in this region.</b> | |||
It is best to have a dedicated S3 bucket for each region you create an environment for, due to the cost of inter-region data transfer. | |||
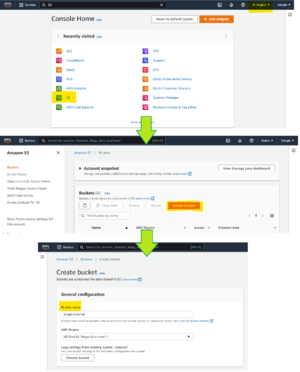
[[File:Awsdock-Step3-flowchart.png|thumb|Diagram explaining how to create an S3 bucket. Note the region- N.Virginia aka us-east-1. This is the optimal region for running docking.]] | |||
=== First time setup === | |||
If it is your first time setting up an environment on your AWS account, you will need to run initialize-aws-batch.bash. This script only needs to be run once per account. | |||
<nowiki> | <nowiki> | ||
root@f54f423d64b1:/home/awsuser/aws-setup# bash | root@f54f423d64b1:/home/awsuser/aws-setup# bash initialize-aws-batch.bash</nowiki> | ||
You should see this script spit out a bunch of JSON text. If you accidentally run this script when it has already been run before, you may see a bunch of errors along the lines of: "Service role name <blank> has been taken in this account". Don't worry about these, they don't mean anything. | |||
== Environment Creation == | |||
<nowiki> | |||
root@f54f423d64b1:/home/awsuser/aws-setup# bash create-aws-batch-env.bash /home/awsuser/awsdock/aws-setup-configs/awsdock_quickstart.config</nowiki> | |||
The quickstart configuration will name your environment "dockenv-us-east-1". This name serves as the unique identifier for this environment, you'll refer to it later when submitting jobs. If you try to create an environment that already exists with the same name, the script will update the existing environment instead of creating a new one. | |||
<b>If you would like to set up an environment with a different name or based in a region other than us-east-1, you can use aws-setup-configs/awsdock.config instead.</b> | |||
Attach the bucket you created to the environment. Don't qualify this with the s3:// path, just the plain name. | |||
[[File:Step6.png|none|x150px]] | |||
Set MAX_CPUS for your environment to desired value. This parameter refers to the maximum number of jobs that can be run in parallel. You should set this at or below the suggested value- this value is derived from the AWS imposed resource limit. You can learn more about resource limits and how to increase them at this page: [[Docking_Submission_On_AWS#Resource_Limits]] | |||
Set BID_PERCENTAGE for your environment to desired value. See section below for more explanation of this parameter, it can potentially save you money. If you're not sure, keep the default. | |||
[[File:Stepwhatever2.png|x119px|Prompts where you will set MAX_CPUS and BID_PERCENTAGE are highlighted]] | |||
=== Bid Percentage === | |||
In order to save money, our AWS batch environment uses the "spot" allocation strategy, which allows us to bid on compute resources at a discount. | |||
The BID_PERCENTAGE parameter indicates what % of the on-demand price our environment is willing to pay for compute resources. At 50%, the environment will wait for at least a 50% discount of the on-demand price to be available before purchasing resources. At 100%, the environment will pay lower prices when they're available, but failing that will pay the full on-demand price. This is the best option for those that want to save money but also don't want to waste time. | |||
== Advanced Usage == | |||
For advanced usage of the aws-setup tool, see here: [[AWS DOCK Environment Setup Advanced Usage]] | |||
[[Category:AWS]] | |||
[[Category:DOCK 3.8]] | |||
[[Category:Tutorial]] | |||
Latest revision as of 20:38, 19 October 2022
- Tutorial 1 AWS:Set up account THIS TUTORIAL
- Tutorial 2: AWS:Upload files for docking
- Tutorial 3: AWS:Submit docking job
- Tutorial 4: AWS:Merge and download results
- Tutorial 5: AWS:Cleanup
Installation
Docker is required to run the aws-setup scripts. https://www.docker.com/get-started/. You can install docker desktop to your personal machine, or log on to a machine where docker is already installed.
An Amazon AWS account is also required, with payment attached. https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/create-and-activate-aws-account/
On a linux/mac/windows computer with docker or docker desktop installed, run the following commands in a terminal:
docker pull dockingorg/aws-setup docker run -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock --rm -it dockingorg/aws-setup
Explanation of arguments:
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sockAllows the container to use your system's Docker--rmCleans up the container once you've exited-itRuns the container interactively
It may be necessary to give the container additional privileges. When you enter the image, test this with the following command:
root@f54f423d64b1:/home/awsuser# docker ps
If you get a permission denied error, exit the container and run again with the --privileged option enabled:
docker run --privileged --rm -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock -it dockingorg/aws-setup
Container Environment
The container uses the ubuntu distribution. Some utilities such as curl and vi are installed so you can download files and edit them. You can also install whatever software you like using "apt install", e.g "apt install git".
If you have files you'd like to access from the container, you can link them in using the docker "-v" option. By default we link the docker socket using this option ("-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock"), but you can link any number of directories or files in this manner. For example, if you would like the contents of the "/tmp" directory on your local machine to be available under "/temp" in the docker image, you would add the following option to your "docker run" command: "-v /tmp:/temp", for a final command of:
docker run -v /tmp:/temp -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock --rm -it dockingorg/aws-setup:latest
If you're an advanced user and you'd like to create your own version of the aws-setup image with certain software preinstalled, you can request us for access to the aws-setup repository, which contains the scripts and Dockerfile we use to set up the docker image. You can also build your own image using our aws-setup image as a base.
Quickstart - Creating your first AWS docking environment
Setup
Credentials & Region
When you enter the docker image, you will be in /home/awsuser. There should be two directories in front of you, aws-setup and awsdock. We start off by going into the aws-setup directory and configuring our AWS credentials. (This needs to be done every time you log in to the container)
root@f54f423d64b1:/home/awsuser# cd aws-setup root@f54f423d64b1:/home/awsuser# aws configure
You'll now be prompted to enter your AWS access key ID & AWS secret access key. If you already know what these are you can enter them and move on. If you don't know what your AWS secret key and access key are, follow this tutorial: https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/security/wheres-my-secret-access-key/. Make sure to save your keys somewhere safe that you will remember!!
Next, you'll be prompted on which AWS region you would like to use. If this is your first environment, set the region to us-east-1. Our lab's molecule data S3 bucket (zinc3d) is also located in this region, so this is the most economical region to run docking jobs in, due to the cost of moving data between AWS regions. (see diagram)
More info on regions & region codes here: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/using-regions-availability-zones.html
The last prompt sets the preferred output format- feel free to leave this blank, or set it to "json".
S3 Bucket
An S3 bucket is a virtual hard drive that your AWS resources can access from anywhere. You will need to create one on your account prior to creating your AWS environment. Follow the amazon tutorial on how to do this: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/userguide/create-bucket-overview.html
The quickstart guide will show you how to create an AWS environment in us-east-1, so it is best to create your S3 bucket in this region.
It is best to have a dedicated S3 bucket for each region you create an environment for, due to the cost of inter-region data transfer.
First time setup
If it is your first time setting up an environment on your AWS account, you will need to run initialize-aws-batch.bash. This script only needs to be run once per account.
root@f54f423d64b1:/home/awsuser/aws-setup# bash initialize-aws-batch.bash
You should see this script spit out a bunch of JSON text. If you accidentally run this script when it has already been run before, you may see a bunch of errors along the lines of: "Service role name <blank> has been taken in this account". Don't worry about these, they don't mean anything.
Environment Creation
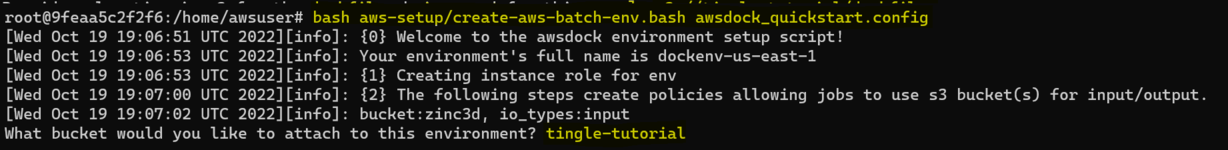
root@f54f423d64b1:/home/awsuser/aws-setup# bash create-aws-batch-env.bash /home/awsuser/awsdock/aws-setup-configs/awsdock_quickstart.config
The quickstart configuration will name your environment "dockenv-us-east-1". This name serves as the unique identifier for this environment, you'll refer to it later when submitting jobs. If you try to create an environment that already exists with the same name, the script will update the existing environment instead of creating a new one.
If you would like to set up an environment with a different name or based in a region other than us-east-1, you can use aws-setup-configs/awsdock.config instead.
Attach the bucket you created to the environment. Don't qualify this with the s3:// path, just the plain name.
Set MAX_CPUS for your environment to desired value. This parameter refers to the maximum number of jobs that can be run in parallel. You should set this at or below the suggested value- this value is derived from the AWS imposed resource limit. You can learn more about resource limits and how to increase them at this page: Docking_Submission_On_AWS#Resource_Limits
Set BID_PERCENTAGE for your environment to desired value. See section below for more explanation of this parameter, it can potentially save you money. If you're not sure, keep the default.
Bid Percentage
In order to save money, our AWS batch environment uses the "spot" allocation strategy, which allows us to bid on compute resources at a discount.
The BID_PERCENTAGE parameter indicates what % of the on-demand price our environment is willing to pay for compute resources. At 50%, the environment will wait for at least a 50% discount of the on-demand price to be available before purchasing resources. At 100%, the environment will pay lower prices when they're available, but failing that will pay the full on-demand price. This is the best option for those that want to save money but also don't want to waste time.
Advanced Usage
For advanced usage of the aws-setup tool, see here: AWS DOCK Environment Setup Advanced Usage