DOCK Blaster:Tutorial 1: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''DOCK Blaster Tutorial 1. Dock to | '''DOCK Blaster Tutorial 1. Dock to Human Thyroid Hormone Receptor Beta-1 (TR beta)''' | ||
[[ | A[[DOCK Blaster:Tutorials | DOCK Blaster Tutorial]]. | ||
==Step 1== | |||
a. Browse to the DOCK Blaster main page: | |||
http://blaster.docking.org/ | |||
and select '''Start with a PDB code''' from the '''DOCK''' pull down menu: | |||
http://blaster.docking.org/parser.shtml | |||
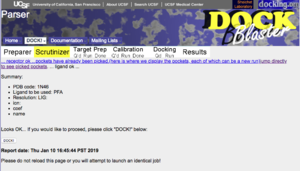
b. In the PDB code field, enter 1N46, the PDB code for TR beta. | |||
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/msd-srv/oca/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1N46 | |||
Click on '''DOCK''' to start. | |||
If you are really impatient you can do all of the above | |||
by simply clicking here: | |||
http://blaster.docking.org/cgi-bin/parser.pl?code=1N46 | |||
= | ==Step 2== | ||
You will get a confirmation page showing that the target has been looked up correctly at the PDB. To proceed, click on "DOCK". Write down the DOCK Blaster Job ID number. You will need it. The docking process is now queued, and may have started if the system is not overloaded. | |||
[[File:DOCK_Blaster_step1a.png|300px|center]] | |||
==Step 3== | |||
Click on the link to browse progress at the bottom of the page | |||
http://blaster.docking.org/cgi-bin/jobwatch.pl?job_id=35605&pin= | |||
(replace the job number with your actual job number. This one will not work) | |||
Step 4. When the job has finished, you will be in the "Calibration Done" state as shown in the progress bar with the yellow paint near the top of the page. You will see a report that reports how well docking worked. | |||
Step 5. Interpreting the calibration summary table | |||
Step 6. Inspecting further details and poses of the ligand and decoys. | |||
Step 7. Launching a docking job | |||
= Literature Cited = | = Literature Cited = | ||
We refer you to our publications pages for theory and practice of docking and virtual screening. | We refer you to our publications pages for theory and practice of docking and virtual screening. | ||
Document status: working tutorial. Please correct any errors you may find. | Document status: working tutorial. Please correct any errors you may find. | ||
[[Category:DOCK Blaster]] | [[Category:DOCK Blaster]] | ||
[[Category:Tutorials]] | [[Category:Tutorials]] | ||
Latest revision as of 02:22, 11 January 2019
DOCK Blaster Tutorial 1. Dock to Human Thyroid Hormone Receptor Beta-1 (TR beta)
Step 1
a. Browse to the DOCK Blaster main page:
http://blaster.docking.org/ and select Start with a PDB code from the DOCK pull down menu: http://blaster.docking.org/parser.shtml
b. In the PDB code field, enter 1N46, the PDB code for TR beta.
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/msd-srv/oca/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1N46 Click on DOCK to start.
If you are really impatient you can do all of the above
by simply clicking here:
http://blaster.docking.org/cgi-bin/parser.pl?code=1N46
Step 2
You will get a confirmation page showing that the target has been looked up correctly at the PDB. To proceed, click on "DOCK". Write down the DOCK Blaster Job ID number. You will need it. The docking process is now queued, and may have started if the system is not overloaded.
Step 3
Click on the link to browse progress at the bottom of the page
http://blaster.docking.org/cgi-bin/jobwatch.pl?job_id=35605&pin= (replace the job number with your actual job number. This one will not work)
Step 4. When the job has finished, you will be in the "Calibration Done" state as shown in the progress bar with the yellow paint near the top of the page. You will see a report that reports how well docking worked.
Step 5. Interpreting the calibration summary table
Step 6. Inspecting further details and poses of the ligand and decoys.
Step 7. Launching a docking job
Literature Cited
We refer you to our publications pages for theory and practice of docking and virtual screening. Document status: working tutorial. Please correct any errors you may find.